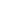WHAT IS MELASMA?
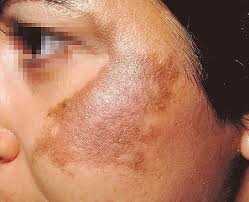
Melasma is an acquired and common skin condition causing discolouration or hyperpigmentation of the skin.
It is often appears symmetrically, occurring predominantly on the face with colour variations ranging from light to dark brown/grey patches.
Melasma ranges from brown (epidermal) to grey/brown(dermal) and a woods lamp assists in identification of the depth of pigment.
When it appears on the face it may present in what is described as a ‘butterfly pattern’ with symmetry on both sides and is commonly referred to as the ‘mask of pregnancy’.
Melasma sufferers are 90% female occurring in the 20-50 year old age group, although uncommon men may also be affected. It is more common in people of Hispanic ,Asian ,Middle Eastern or Latin heritage.
CAUSES
-
Sun exposure
-
Pregnancy (Chloasma)
-
Oral contraceptive
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Certain epilepsy drugs
-
Hyperthyroidism é levels of circulating hormone
-
Heat- condition exascacerbated in summer months, heat +sun exposure +genetics=worsening of the condition
-
Hormones-é levels of progesterone
-
Products irritating to the skin
Melasma is thought to have many contributing factors.
Studies have shown that post menopausal women who receive progesterone therapy are more likely to develop melasma than those who are receiving eostrogen alone.
Treatments and products which irritate the skin may increase melanin production worsen the condition.
Some hair removal techniques such as waxing may irritate the skin contributing to hyperpigmentation.
An increase in melanin, melanocytes and melanosomes in addition to an increase in capillary network has been found in melasma affected skin.
Treatments shown to have proven results with clearance in 60-80% of sufferers, are those that take a combination approach.
Unfortunately Melasma may be slow to respond taking up to 8 weeks to see improvement. Epidermal Melasma responds better to treatments as the pigment is closer to the surface of the skin.
TREATMENT OPTIONS
-
Depigmenting agents-Hydroquinone, Retinoids, Kojic Acid, Azelaic Acid, Ascorbic Acid
-
Chemical Peels-AHA peels, formulations including Glycolic and Lactic
-
Lasers or Light Based Therapies
Depigmenting agents are applied topically in a cream formula and contain Hydroquinone, Retinoids, Kojic Acid, Azelaic Acid, Ascorbic Acid and Corticosteroids.These agents may be used alone or in a more effective combination formula where three or more agents are combined.
Most lightening agents may be purchased over the counter. Hydorquinone in concentrations over 2% must be prescribed by a Doctor.
Increasing the strength of HQ increases the risk of skin irritation.
Kligmans Formula and Tri-Luma are triple combination creams containing Hydroquinone, Retinoids and a Corticosteroid. These triple creams have shown to be very effective in the treatment of Melasma but should not be used for prolonged periods of time or be used by pregnant or lactating women. This triple combination therapy has been shown to be more effective than using HQ alone.
Studies have shown the results are not as significant when using Azealaic,Kojic,Ascorbic and Soy Bean as lightening agents compared to the results of the Tri Cream containing Hydroquinone 4% .
There is discussion around the Soy Isolflavone, Genistein, which is commonly used in lightening products. It is effective when used in lightening pigmentation caused by sun damage but it is not suitable to use in treating Melasma as it is a phytoestrogen and Melasma, in some cases, is triggered hormonally.
Chemical peels are another treatment option to consider and vary in strength and depth of penetration and should be tailored to skin type. Combinations of Glycolic and Lactic acids have been found useful in treating Melasma exfoliating the superficial layers of the skin.
Lasers and light based therapies can also be used in treating Melasma but should be used with caution as they may worsen some types of Melasma.
Microdermabrasion uses vacuun suction together with an abrasive material such as alluminium oxide crystals.It exfoliates the superficial layers of the skin reducing the appearance of the discolouration. The suction and abrasion is adjusted according to the skin tolerance.
All treatments are progessive treatments and require multiple treatments to be effective and compliance when using sunscreen.
The Good News…
Although a chronic skin condition and for some sufferers psychosocially worrying. Melasma can be controlled but it is a slow process, so establishing the right management commensurate with the correct diagnosis is an integral part in treating the condition. Best results are observed with a multifactorial approach including a combination of therapies.
The Bad News…
Long term use of HQ is dissuaded as it can lead to a condition referred to as Ochronisis ,which is a permanent skin discolouration. This condition is seen in HQ preparations of 4% and higher and use should be ceased immediately signs appear.
Melasma may be slow to respond to treatment and unfortunately some treatment options which provide the best results create localised skin irritations such as itching ,redness, peeling,dry skin and hyperpigmentation.
New developments in sight…
BMC Dermatology reported a new study involving Silymarin Cream-a deriviative of the Milk Thistle plant which prevenst melanin production. All patients participating in the study reported significant improvement of their Melasma in lesion colour and size reduction from the first week with no reported side effects. The study concluded Silymarin was a safe and effective treatment for Melasma.
New oral medications are under investigation but none are available at this time.
http://blogs.webmd.com/healthy-skin/2011/11/the-soy-effect.html
http://www.amjorthopedics.com/fileadmin/qhi_archive/ArticlePDF/CT/075010057.pdf
http://dermnetnz.org/colour/melasma.html
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/777689
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/549273_3